
Systemic signs include dental abnormalities including a congenital condition in which fewer teeth than normal are present (hypodontia), a tooth or teeth that are smaller than normal (microdontia), six or more missing teeth (oligodontia), complete absence of teeth (anodontia) and/or cone-shaped teeth. Defects in the formation of the angle of the eye and/or adhesions that block this drainage route that are associated with ARS can lead to glaucoma. Fluid in the eye normally drains out of the eye through the angle formed by the junction of the iris and the cornea. Glaucoma is seen in approximately 50% of patients with ARS and can lead to complete permanent blindness if not treated. This damage is often secondary to increased pressure within the eyeball. Glaucoma is a group of diseases in which the eye’s optic nerve is damaged. Other features include adhesions in the front of the eye, between the iris and the edge of the cornea.
PETERS ANOMALY FULL
The main ocular signs include an underdeveloped iris (iris hypoplasia), displacement of the pupil of the eye so that it is not centered (corectopia), one or more full thickness tears in the iris of the eye and an opaque ring around the outer edge of the cornea (posterior embryotoxon).

Ocular features of ARS usually occur in both eyes. Thus, they are now all grouped under the same condition referred to as Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome. Distinction between these four conditions was difficult and clinically irrelevant due to the overlap of clinical features between them as well as the involvement of the same gene changes (mutations). Later in 1934, Rieger described the Rieger anomaly as central changes in the iris of the eye along with features mentioned in Axenfeld anomaly.Īxenfeld syndrome and Rieger syndrome are defined as Axenfeld anomaly and Rieger anomaly accompanied by systemic effects, respectively. The Axenfeld anomaly is defined as eye peripheral anterior segment defects and was first described in 1920 by the German ophthalmologist Theodor Axenfeld. Thus, the main course of treatment is the effective management of glaucoma, medically or surgically (if medications are not effective). Glaucoma is often due to increased fluid pressure within the eyeball and can lead to complete permanent blindness if left untreated. A serious consequence of ARS is glaucoma, which usually develops later in childhood or adulthood.
PETERS ANOMALY SKIN
Non-ocular features include, among others, dental and craniofacial abnormalities, hearing loss, excessive skin around the navel and very rarely a smaller than usual anal opening (refer to the ‘Signs & Symptoms’ section of this report for more information).ĪRS is the result of abnormal embryonic development, so the condition is usually diagnosed during infancy or childhood.
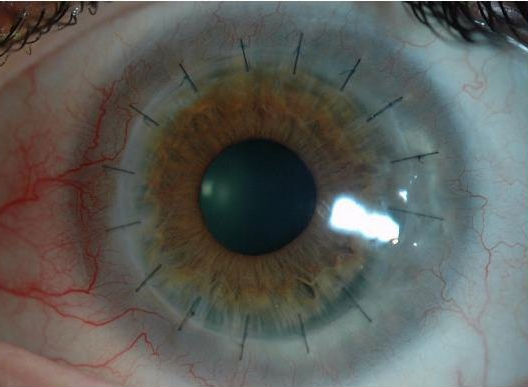
Ocular features include, among others, an underdeveloped iris (iris hypoplasia), displacement of the pupil of the eye so that it is not centered (corectopia), full thickness tears in the iris of the eyes, an opaque ring around the outer edge of the cornea (posterior embryotoxon) and very rarely a small cornea (microcornea). Signs and symptoms of ARS can be divided into ocular and non-ocular (systemic).

The disorder affects males and females equally and has been observed in patients from various ethnic backgrounds from all over the world. It is estimated to occur in approximately 1 person in 50,000 worldwide. 5 Myths About Orphan Drugs and the Orphan Drug ActĪxenfeld-Rieger syndrome (ARS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the eye as well as other parts of the body.Information on Clinical Trials and Research Studies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
